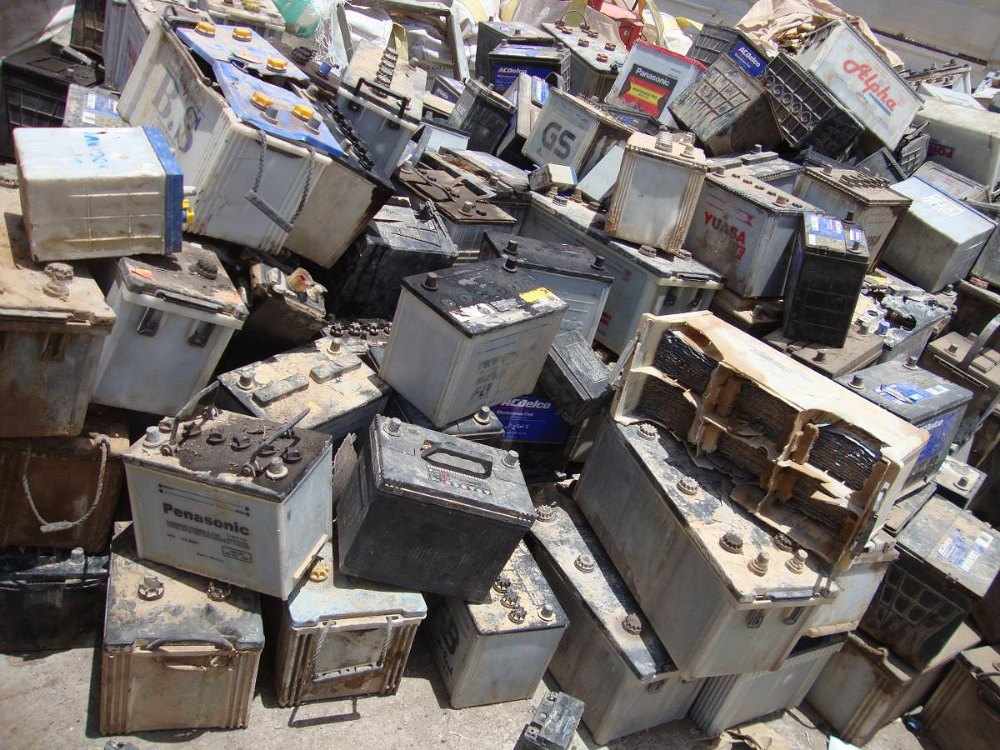

Introduction
The Used Lead Acid Batteries (ULAB) Market is experiencing robust growth in 2025, propelled by stringent environmental regulations, the rise of electric mobility, and advancements in recycling technologies. ULABs, primarily sourced from automotive, industrial, and energy storage applications, are a critical component of the circular economy due to their high recyclability. Recent developments, such as new recycling facilities and the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions, are shaping the market’s trajectory. This article explores the key drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the ULAB market, drawing on the latest industry insights.
Rising Demand for Electric Mobility
The global surge in electric vehicle (EV) adoption, including e-bikes and hybrid vehicles, is a significant driver of the ULAB market in 2025. Lead-acid batteries remain a cost-effective and reliable power source for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) systems in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and auxiliary systems in EVs. The increasing use of e-bikes, particularly in regions like Southeast Asia and China, is generating substantial volumes of ULABs, as these vehicles rely heavily on lead-acid batteries. Recent reports indicate that e-bike batteries dominate the recyclable lead-acid battery market in China, with stable procurement prices reflecting strong demand.
The expansion of electric mobility is also supported by the growing need for energy storage in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power. ULABs are widely used in off-grid solar solutions, particularly in high-growth regions like Africa and Southeast Asia, where electrification is accelerating. This trend is driving the generation of used batteries, bolstering the supply chain for recyclers and supporting the ULAB market’s growth.
Advancements in Recycling Technologies
Technological innovations in lead recovery are transforming the ULAB market. In 2025, the industry is witnessing a shift toward secondary production, with recycled lead contributing to over half of the global supply. Companies like Gravita India have recently commissioned new recycling facilities, such as the one in Rewari, Rajasthan, which boosts processing capacity significantly. These facilities employ advanced smelting and refining techniques to recover lead with higher efficiency and lower environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Innovations in battery design, such as enhanced grid structures and alloy compositions with calcium and tin, are improving the recyclability of lead-acid batteries. The formalization of recycling processes, driven by extended producer responsibility (EPR) regulations, is further enhancing the efficiency of ULAB collection and processing. These advancements are reducing the environmental footprint of lead-acid batteries, making them a sustainable option for energy storage and supporting market growth.
Environmental Regulations and Circular Economy
Stringent environmental regulations are a key driver of the ULAB market. Governments worldwide are implementing policies to ensure proper disposal and recycling of lead-acid batteries due to the hazardous nature of lead. The Battery Council International reports that millions of metric tons of ULABs are produced annually, necessitating robust recycling frameworks. In 2025, the push for circular economy practices is encouraging manufacturers to invest in closed-loop recycling systems, where recovered lead is reused in new battery production.
In Europe, where over 30 million EVs are expected on the roads, regulations are driving the formalization of ULAB recycling. Similar trends are observed in Asia-Pacific and Africa, where expanding electrification and off-grid energy solutions are increasing ULAB volumes. These regulations not only mitigate environmental risks but also create opportunities for recyclers to meet the growing demand for secondary lead, further fueling the market.
Regional Dynamics and Market Expansion
Asia-Pacific dominates the ULAB market, with China accounting for a significant share due to its vast manufacturing infrastructure and high e-bike usage. Recent reports from the Shanghai Metal Market highlight stable procurement prices for waste e-bike batteries, indicating a mature recycling ecosystem. India is also emerging as a key player, with companies like Gravita India expanding recycling capacity to meet domestic and global demand.
In North America, particularly the U.S., a strong recycling infrastructure supports the ULAB market, driven by the widespread use of lead-acid batteries in automotive and industrial applications. Europe remains a leader in regulatory frameworks, with countries like Germany and the UK investing in advanced recycling technologies. Africa and Southeast Asia are high-growth regions, where off-grid solar solutions and electrification are accelerating ULAB generation, creating opportunities for market expansion.
Challenges Facing the Market
The ULAB market faces several challenges. China’s restrictions on critical minerals like antimony, a key component in lead-acid batteries, are creating supply chain disruptions. These restrictions, implemented in late 2024, have increased procurement costs, affecting recyclers and manufacturers. The reliance on informal recycling networks in some regions, particularly in developing economies, poses environmental and safety risks, as improper handling of ULABs can lead to lead contamination.
Competition from lithium-ion batteries, which offer higher energy density and longer lifespans, is another challenge. While lead-acid batteries remain cost-effective, the shift toward advanced battery chemistries in EVs and energy storage systems could limit long-term ULAB growth. Additionally, the need for skilled personnel and advanced infrastructure to handle modern recycling processes is a barrier in some markets.
Opportunities for Growth
The ULAB market offers significant opportunities, particularly in sustainable recycling and energy storage. The growing adoption of renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind, is increasing demand for cost-effective storage solutions, where lead-acid batteries excel. The development of advanced recycling technologies, such as hydrometallurgical processes, presents opportunities to improve lead recovery rates and reduce environmental impact.
The expansion of EPR regulations and government incentives for sustainable practices are creating new avenues for investment. In high-growth regions like Southeast Asia and Africa, the increasing deployment of off-grid solar solutions is driving ULAB volumes, offering recyclers a chance to scale operations. Partnerships between manufacturers and recyclers are also fostering innovation, ensuring the ULAB market remains competitive.
Industry Leaders and Competitive Landscape
Key players like EnerSys, GS Yuasa Corporation, and Gravita India are leading the ULAB market through investments in recycling infrastructure and advanced battery technologies. EnerSys is focusing on enhanced flooded batteries (EFBs) and absorbent glass mat (AGM) systems, which improve recyclability and performance. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions are helping these companies expand into emerging markets, while innovations in lead recovery are strengthening their competitive edge.
Conclusion
In 2025, the Used Lead Acid Batteries (ULAB) market is thriving, driven by electric mobility, recycling innovations, and stringent environmental regulations. The rise of e-bikes, renewable energy systems, and circular economy practices is fueling ULAB generation and recycling, while companies like Gravita India lead with advanced facilities. Despite challenges like supply chain disruptions and competition from lithium-ion batteries, opportunities in sustainable recycling and energy storage signal a robust future. As global demand for cost-effective and eco-friendly solutions grows, the ULAB market is poised to play a pivotal role in the energy transition.



















Write a comment ...